library(tidyverse)
library(readxl)
path = "files/CH-176 Custom Grouping.xlsx"
input = read_excel(path, range = "B2:C27")
test = read_excel(path, range = "F2:G7")
result = input %>%
mutate(Group = rep(1:ceiling(nrow(input)/5), each = 5)) %>%
summarise(Quantity = sum(Quantity), .by = Group)
all.equal(result, test, check.attributes = FALSE)
#> [1] TRUEOmid - Challenge 176
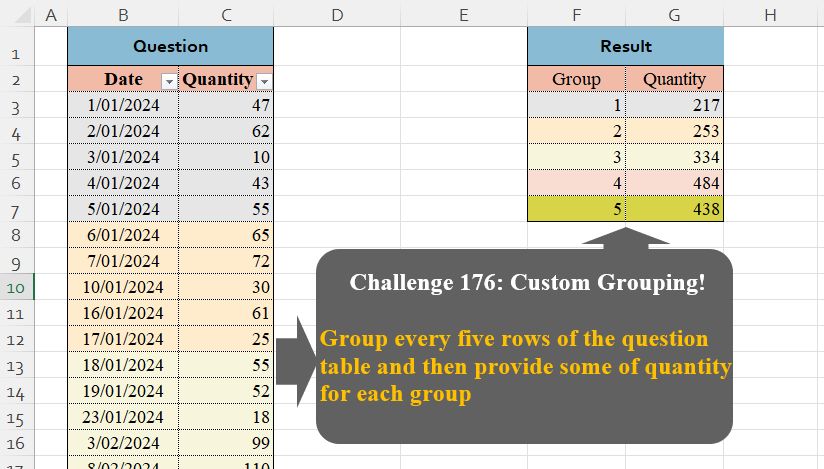
Challenge Description
🔰Group every five rows of the question table and then provide some of quantity for each group
Solutions
Logic:
rep(1:ceiling(nrow(input)/5), each = 5): Divides the rows into groups of five by generating a group number for each row.summarise: Aggregates the sum ofQuantityfor each group.
Strengths:
Compactness: Uses concise tidyverse functions to group and aggregate.
Flexibility: Dynamically adapts to any number of rows in the input data.
Areas for Improvement:
- Incomplete Last Group: Ensure the last group works correctly if it has fewer than 5 rows (handled by
ceilinghere).
- Incomplete Last Group: Ensure the last group works correctly if it has fewer than 5 rows (handled by
Gem:
- The use of
repto dynamically create grouping indices is an efficient approach.
- The use of
import pandas as pd
path = "CH-176 Custom Grouping.xlsx"
input = pd.read_excel(path, usecols="B:C", skiprows=1, nrows=26)
test = pd.read_excel(path, usecols="F:G", skiprows=1, nrows=5).rename(columns=lambda x: x.split('.')[0])
input['Group'] = (input.index // 5) + 1
result = input.drop(columns=['Date']).groupby('Group').sum()
result.reset_index(inplace=True)
print(result.equals(test)) # TrueLogic:
(input.index // 5) + 1: Divides the rows into groups of five by calculating the group number based on the row index.groupby('Group').sum(): Aggregates the sum ofQuantityfor each group.reset_index: Resets the index for a clean final output.
Strengths:
Simplicity: The logic is straightforward and easy to understand.
Adaptability: Works seamlessly with datasets of varying row counts.
Areas for Improvement:
- None; the logic handles both complete and incomplete groups effectively.
Gem:
- The use of
(input.index // 5) + 1to generate group indices is simple yet effective.
- The use of
Difficulty Level
This task is easy to moderate:
- It involves basic row grouping and summation, but requires some understanding of indexing and grouping operations.