library(tidyverse)
library(readxl)
path = "Excel/630 Immediate Last Caller.xlsx"
input = read_excel(path, range = "A1:C16")
test = read_excel(path, range = "D1:D16")
result = input %>%
mutate(`Answer Expected` = order_by(Time, lag(Caller)), .by = Date)
all.equal(result$`Answer Expected`, test$`Answer Expected`)
[1] TRUE Excel BI - Excel Challenge 630
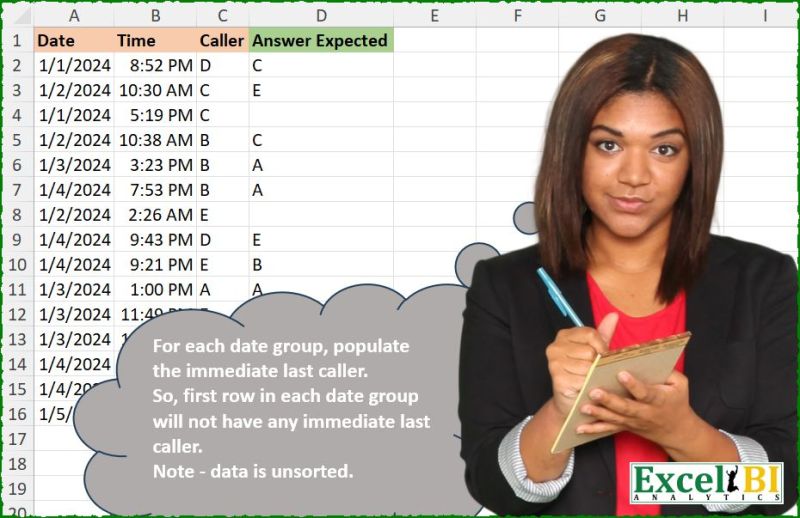
Challenge Description
For each date group, populate the immediate last caller. So, first row in each date group will not have any immediate last caller. Note - data is unsorted.
Download Practice File - https://lnkd.in/dwFEQgce
Solutions
Logic:
mutate: Adds a new column (Answer Expected) that contains the immediate last caller.
order_by(Time, lag(Caller)): Ensures that the data is sorted by Time before applying the lag function to fetch the previous value.
.by = Date: Groups the data by Date, so the lag function only applies within each group.
Strengths:
Conciseness: Combines sorting and lagging in a single step with order_by.
Readability: Leverages tidyverse functions, which are intuitive and readable.
Areas for Improvement:
- Edge Case Handling: Ensure that Time and Date are valid and properly formatted to avoid errors.
Gem:
- Using order_by(Time, lag(Caller)) is a clean and efficient way to sort and fetch the previous value in one step.
import pandas as pd
path = "630 Immediate Last Caller.xlsx"
input = pd.read_excel(path, usecols="A:C", nrows=16)
test = pd.read_excel(path, usecols="D", nrows=16)
input['Answer Expected'] = input.sort_values(by='Time').groupby('Date')['Caller'].shift()
print(input['Answer Expected'].equals(test['Answer Expected'])) # TrueLogic:
sort_values(by='Time'): Sorts the data chronologically within each date group.groupby('Date')['Caller'].shift(): Fetches the previous caller in the sorted order for each date group.shift(): Handles the logic for getting the “immediate last caller,” leaving the first row asNaN.
Strengths:
Step-by-Step Clarity: Each operation is explicit and modular, making the logic easy to follow.
Accuracy: The use of
sort_valuesensures the correct chronological order within groups.
Areas for Improvement:
Efficiency: Sorting can be computationally expensive for large datasets, but it’s necessary for this task.
Flexibility: Assumes the
Timecolumn is correctly formatted and sortable.
Gem:
- The use of
groupbywithshift()directly mirrors the task requirement in an intuitive and concise way.
- The use of
Difficulty Level
This task is of moderate complexity:
- It involves knowledge of regular expressions, which can be challenging for beginners.
- The task requires dynamic replacement logic, which adds an extra layer of difficulty.