library(tidyverse)
library(readxl)
path = "files/Ex-Challenge 04 2025.xlsx"
input = read_excel(path, range = "B3:D18")
test = read_excel(path, range = "F3:G13")
result = input %>%
mutate(Rank = dense_rank(desc(Demand))) %>%
summarise(`Fruit(s)` = paste0(Fruit, collapse = " ; "), .by = Rank) %>%
arrange(Rank)Crispo - Excel Challenge 04 2025
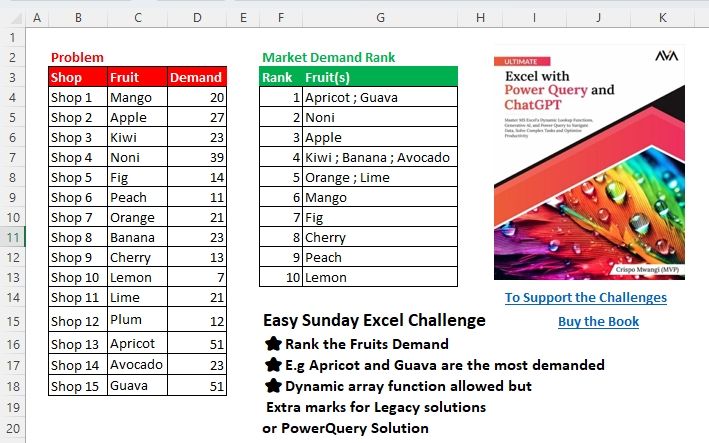
Challenge Description
Easy Sunday Excel Challenge
⭐Rank the Fruits Based on Demand
⭐ e.g. Apricot and Guava are the most demanded
Solutions
Logic:
- Calculate Rank: Use
dense_rank(desc(Demand))to assign ranks in descending order, ensuring that fruits with the same demand get the same rank.
Group by Rank: Use
summariseto concatenate fruit names (paste0(Fruit, collapse = " ; ")) for fruits with the same rank.Sort the Data: Arrange the data by rank in ascending order to maintain ranking consistency.
- Calculate Rank: Use
Strengths:
- Efficient Ranking: Uses
dense_rank(desc(Demand)), which assigns the same rank to identical demand values.
Concatenation of Fruits: Uses
paste0(Fruit, collapse = " ; ")to properly format the result.Readable and Compact: The pipeline approach (
%>%) ensures clarity and modularity.
- Efficient Ranking: Uses
Areas for Improvement:
- Formatting: Consider checking for duplicate separators (e.g., extra spaces or semicolons).
- Scalability: If demand values are floating-point numbers instead of integers, precision issues might arise.
Gem:
- The use of
dense_rank(desc(Demand))ensures an accurate ranking system that avoids gaps in ranking.
- The use of
import pandas as pd
path = "files/Ex-Challenge 04 2025.xlsx"
input = pd.read_excel(path, usecols="B:D", skiprows=2, nrows=15)
test = pd.read_excel(path, usecols="F:G", skiprows=2, nrows=10)
result = input.assign(Rank=input['Demand'].rank(method='dense', ascending=False).astype(int)) \
.groupby('Rank')['Fruit'].agg(' ; '.join) \
.reset_index() \
.sort_values(by='Rank')Logic:
- Calculate Rank: Use
rank(method='dense', ascending=False).astype(int)to rank fruits based on demand in descending order.
Group by Rank: Use
.groupby('Rank')['Fruit'].agg(' ; '.join)to concatenate fruits sharing the same rank.Sort the Data: Sort by
Rankto maintain ranking consistency.
- Calculate Rank: Use
Strengths:
- Efficient Ranking: Uses
rank(method='dense', ascending=False).astype(int)to ensure consecutive ranking without gaps.
Concatenation of Fruits: Uses
.groupby('Rank')['Fruit'].agg(' ; '.join)to merge fruit names within the same rank.Concise and Vectorized: Uses
assignfor ranking andgroupbyfor aggregation, ensuring efficient execution.
- Efficient Ranking: Uses
Areas for Improvement:
- Edge Cases: Ensure that fruit names are properly formatted and no unintended characters are introduced.
- Scalability: If the dataset is very large, consider optimizing string concatenation to avoid performance bottlenecks.
Gem:
- The combination of
rank(method='dense', ascending=False).astype(int)andgroupbymakes ranking and aggregation highly efficient.
- The combination of
Difficulty Level
This task is moderate:
- Requires reshaping and aggregating data, which are common but non-trivial transformations.
- Demands familiarity with ranking methods and handling ties in numerical data.
- Involves string manipulation to concatenate multiple fruit names within the same rank.
- Requires careful sorting to ensure correct order of ranked results.